Table of Content
- Outdated Construction Norms
- Smart Roofing Solutions for Energy Efficiency and Climate Control
- Why Investing in Smart Roofing Brings Long-Term Benefits
- New Priorities in Sourcing Roofing Materials
Outdated Construction Norms
Summer of 2025 is bringing record highs, with temperatures of over 40°C across Europe.
These events are not single anomalies but the effects of climate change, impacting the livability and performance of buildings, especially in densely populated urban areas.
Cities like Paris, Madrid, and Rome are particularly vulnerable because of the “urban heat island” effect: Asphalt, roofing materials, and concrete absorb heat during the day and release it at night, making nighttime cooling difficult.
As a result, buildings constructed under outdated thermal standards are becoming problematic both in performance and compliance.
To counteract, governments are strengthening regulatory frameworks to reduce overheating in residential and commercial buildings.
France’s Loi Climat, for example, allows authorities to classify properties as unfit for rental if they fail to meet indoor thermal comfort standards. In such cases, these buildings must be removed from the rental market.
The new laws clearly show that legacy building norms no longer align with upcoming climate realities, highlighting the need for more advanced cooling strategies.
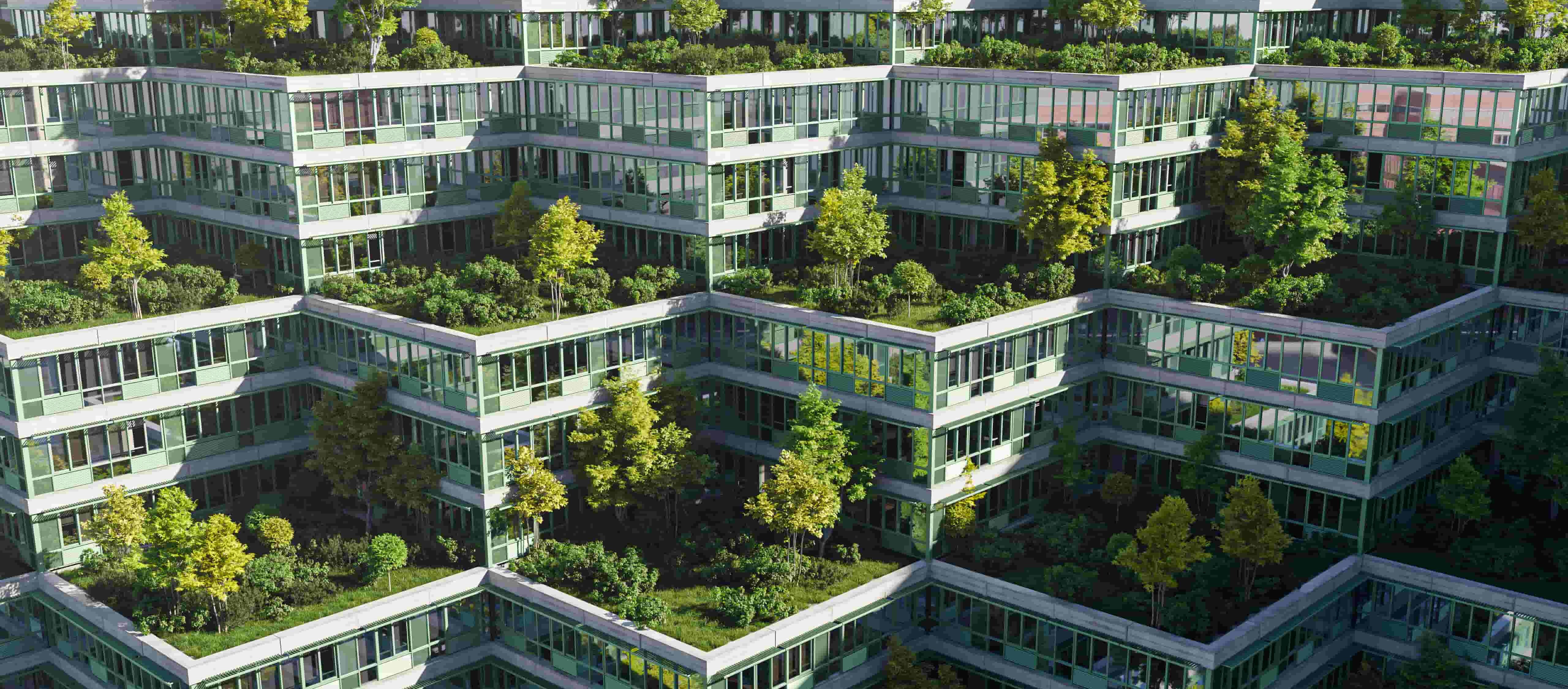
Smart Roofing Solutions for Energy Efficiency and Climate Control
Smart roofing is becoming a popular and practical solution for managing building temperatures and meeting updated energy regulations.
Unlike conventional roofing systems, smart roofs are made from materials and technologies that respond dynamically to solar radiation and outdoor conditions.
Overview of Smart Roofing Technologies
| Smart Roofing Type | Description | Key Benefits |
| Cool Roofs | Made of highly reflective materials such as white membranes, polymer coatings, or light-colored tiles to reflect sunlight and reduce heat absorption. | - Lowers roof temperature by up to 30°C - Reduces AC demand and energy bills - Extends roof life |
| Green Roofs | Use vegetation and soil layers to insulate buildings, manage rainwater, and lower surface temperatures. Ideal for dense urban areas with limited green space. | - Natural insulation - Urban cooling and biodiversity - Rainwater management |
| Phase-Change Materials (PCMs) | Use substances that absorb and release heat during phase transitions (solid ↔ liquid) to help regulate indoor temperature. | - Maintains stable indoor climate - Reduces heating and cooling needs |
Some smart roofs include IoT sensors that track surface temperature, moisture levels, and energy performance in real time. This data is used to optimize building management and support compliance with energy regulations.
Outside of Europe, large-scale implementations are already proving to be successful:
In Singapore, reflective coatings applied to public housing rooftops have reduced surface temperatures by 4–5°C.
In California, the Title 24 Energy Efficiency Standards have made cool roofs mandatory in certain climate zones, which has led to their wide use in the commercial sector.
As smart roofing systems become a key component of modern construction and property management, now is the ideal moment to connect with reliable suppliers and discover innovative new materials.
Why Investing in Smart Roofing Brings Long-Term Benefits
Shifting to heat-resilient building practices brings both challenges and opportunities for companies in the construction and real estate sectors.
Smart roofing systems can raise project costs, depending on the solution:
- Reflective coatings are the most budget friendly.
- Green roofs and phase-change material (PCM) systems cost more to install and maintain.
- Retrofitting older buildings can be tricky, especially if the structure can’t support extra weight.
Still, the long-term benefits often make the investment worthwhile. Smart roofing helps buildings to improve their energy ratings and provide better indoor comfort.
These advantages can boost property value and make buildings more appealing to tenants. For owners, lower cooling needs mean reduced operating costs and better ESG scores.
Regulations are also getting stricter. To avoid future risks, buildings need to be ready for new energy and climate standards. Properties that don’t comply may face a drop in value, limits on renting and mandatory upgrades.
That’s why many project planners now include smart roofing in the early design stages to stay ahead.
New Priorities in Sourcing Roofing Materials
The growing interest in smart roofing is part of a bigger shift in how building materials are sourced, assessed, and used.
With changing weather patterns and evolving regulations, the market is moving toward more advanced, tech-savvy solutions. Cost and durability are still important, but buyers now have a wider range of factors to consider, such as:
- How well the material works with climate modeling tools
- Whether it can be integrated into digital building management systems
- Its overall environmental impact and potential for certifications like LEED, BREEAM, or HQE
Architects, engineers, urban planners, and data experts are now involved earlier in the process. They're using digital twins and climate simulations to test roofing options before a single tile is laid.
For buyers, this means working with suppliers who can provide not just materials, but also technical data and compliance documentation to support smarter, regulation-ready decisions.
Conclusion
Smart roofing is not only a building upgrade, but a smart move for businesses that want to follow up with new rules and sustainability goals early on.
And as digital tools and climate data become part of everyday planning, early adopters will be better equipped to make informed decisions and manage long-term risks.
For more information on construction and building management, visit europages’ online blog Inside Business to stay up-to-date and discover practical solutions for your projects!
Manufacturer of Heat Pumps Driving EU Decarbonization
Home Security Systems: A Builder's Guide to Modern Solutions

